The rubber liner for ball mill is of great significance in industrial production. The details are as follows:
- Materials and Structure
- Materials: Usually made of high-quality natural rubber, synthetic rubber or rubber composites. Some may add reinforcing agents and fillers to enhance performance, like abrasion resistance and tear resistance.
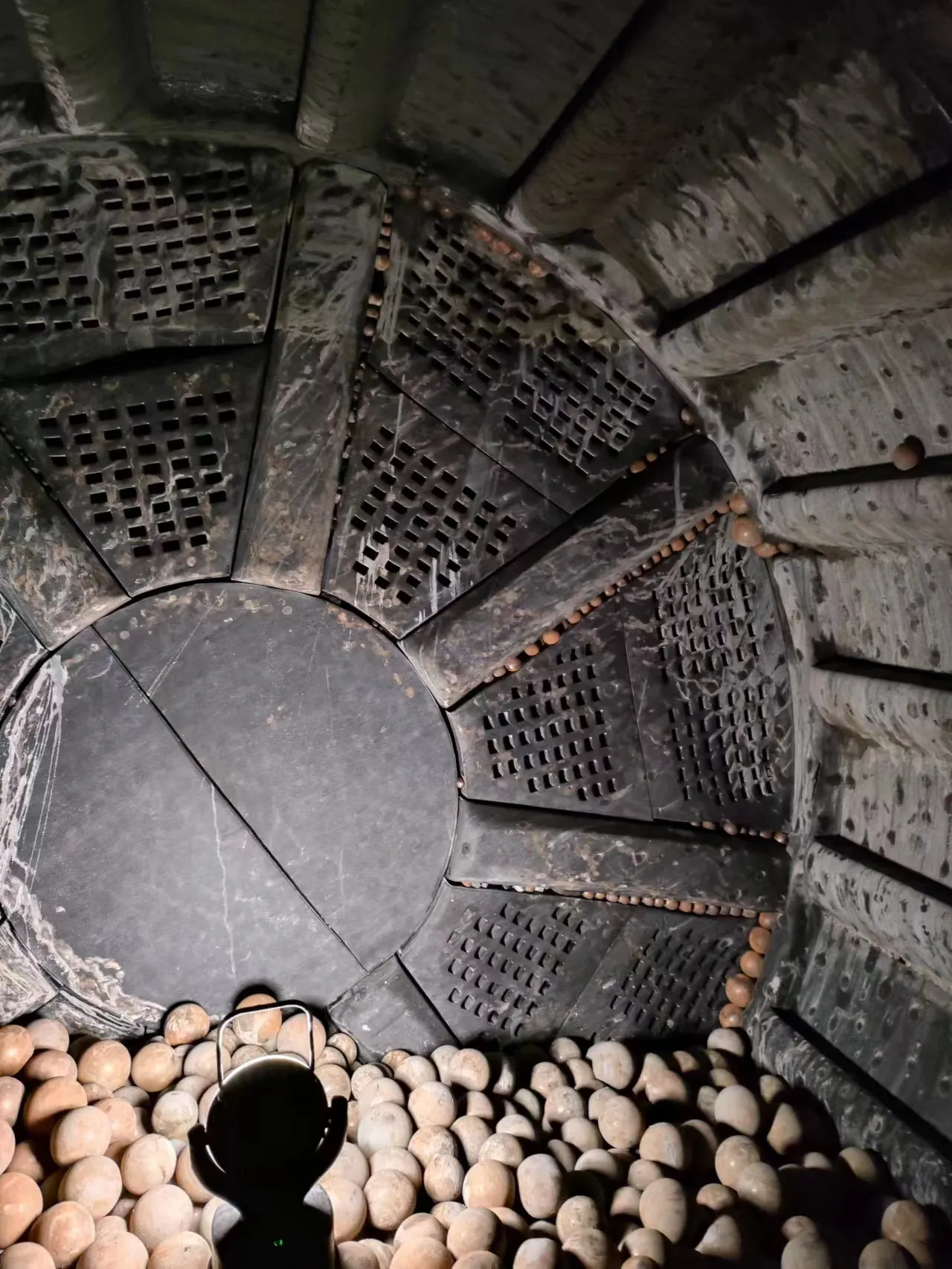
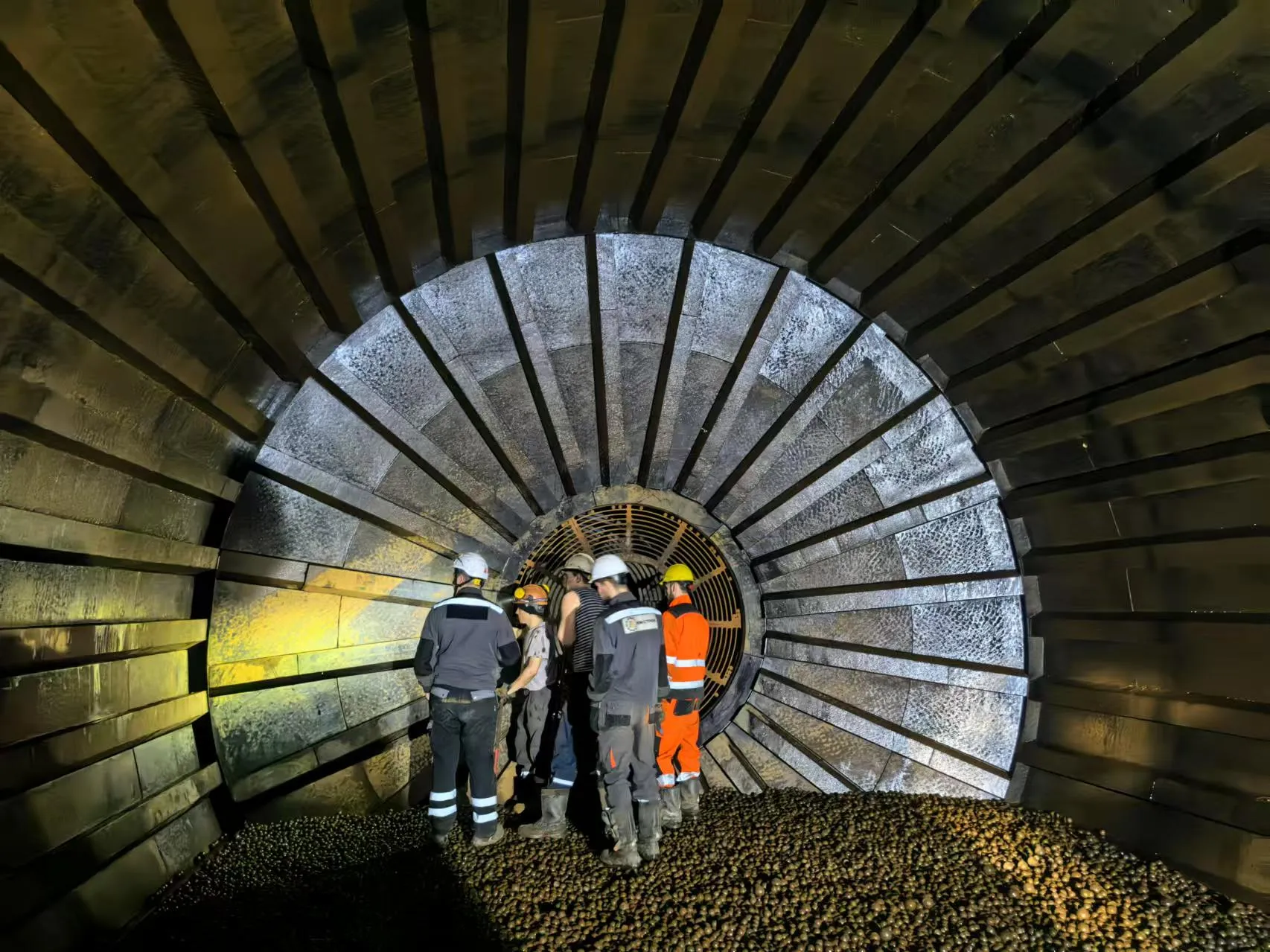
- Structure: Composed of shell plates, head liners and lifter bars. Shell plates cover the inner wall of the ball mill cylinder. Head liners are installed at both ends of the cylinder. Lifter bars are set on the inner wall of the cylinder, which can lift and stir materials and grinding media to improve grinding efficiency.
- Functions and Advantages
- Excellent Protection: Protects the inner shell of the ball mill from direct abrasion and impact of materials and grinding media, prolonging the service life of the mill shell.
- Noise Reduction: The elastic rubber can absorb vibration and impact energy, reducing the noise generated during the ball mill's operation and improving the working environment. It can generally reduce noise by 8-10 dB.
- Energy Saving: With a lower density than metal liners, rubber liners reduce the overall weight of the ball mill, lightening the load on the motor and bearings, thus reducing energy consumption. The energy efficiency of the ball mill can be increased by about 15%.
- Good Sealing Performance: Forms a good seal to prevent slurry leakage and the loss of materials and grinding media, avoiding corrosion of the ball mill shell by the slurry.
- Easy Installation and Replacement: Lightweight and easy to handle, the rubber liners are convenient to install and replace, reducing maintenance time and labor intensity, and increasing the ball mill's availability.
- High Wear Resistance: The wear resistance of rubber liners is 1.5 to 2 times higher than that of manganese steel liners in wet ball mills, and 1.5 to 4 times in some cases, reducing the frequency of liner replacement.
- Applications
- Mining Industry: Commonly used in gold, copper, iron and other ore grinding operations to improve grinding efficiency and reduce equipment wear.
- Metallurgical Industry: Applied in the grinding process of metallurgical raw materials such as iron ore and manganese ore.
- Chemical Industry: Used in the production of chemical raw materials such as pigments, resins and fertilizers that require grinding operations.
- Construction Materials Industry: Can be used in the grinding of cement clinker, gypsum and other materials in cement plants.